La colonne thoracique et les piliers anatomiques
Les 12 vertèbres entre la 7ème cervicale et la 1ère lombaire font partie de l'espace thoracique avec le sternum. On ne peut pas les séparer sans fabriquer des articulations ce qui est contraire a la fonction discale qui est une zone déformable.

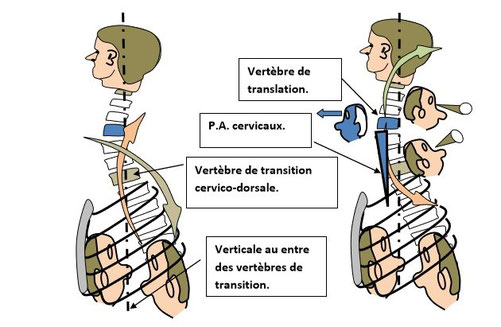
Les flèches montrent la dissociation spino – prévertébrale de part et d’autre de la vertèbre de transition cervico dorsale.
La vertèbre de translation cervicale, définit la position des attaches des piliers anatomiques cervicaux, par rapport à la verticale des vertèbres de transition.
The arrows show the spino-prevertebral dissociation on either side of the cervico-dorsal transition vertebrae.
The cervical translational vertebra defines the position of the attachments of the cervical anatomical pillars in relation to the vertical of the transitional vertebrae.
La vertèbre de translation lombaire définit la position des attaches des piliers anatomiques lombaires par rapport à la verticale des vertèbres de transition.
Ci-dessous dissociation ilio psoïque et dissociation de la musculature spinale postérieure de part et d’autre de l’insertion des piliers anatomiques.
The lumbar translational vertebra defines the position of the lumbar anatomical pillar attachments relative to
the vertical of the transition vertebrae.
Below ilio psoic dissociation and dissociation of the posterior spinal musculature on either side of the insertion of the anatomical abutments.

Ci-dessous angle d’antéversion sacré et positionnement de l’insertion des piliers anatomiques par rapport à la verticale des zones de transition.
Avec a gauche antéversion normale, accentuée au centre, et inversée a droite.
Below is the angle of sacral anteversion and positioning of the anatomical abutment insertion relative to the
vertical of the transition zones.
With left normal anteversion, accentuated in the center, and inverted to the right.

Angle d'antéversion de la vertèbre de transition C7 D1 et positionnement des piliers anatomiques cervicaux.
Anteversion angle of the C7 D1 transition vertebra and positioning of the cervical anatomical abutments.

A gauche espace diaphragme abdomino - pelvien et les piliers anatomiques lombaires.
A droite espace diaphragme intercostaux et les piliers anatomiques cervicaux.
Left abdominal-pelvic diaphragm space and lumbar anatomical pillars.
On the right, intercostal diaphragm space and cervical anatomical pillars.

Les surfaces d’application pressionnelle diaphragmatico – abdominale par rapport aux piliers anatomiques lombaires.

Positionnement a la bissectrice de l’extrémité supérieure du pilier fonctionnel abdominal.
L'image ci dessous utilise les tetes pour faire apparaitre les surfaces d'application pressionnelles, en fonction de la forme du thorax. Ce qui décale les piliers anatomiques au niveau du centre phréniques, ce qui modifie leur rapport a la verticale. Pour fonctionner le diaphragme a besoin d'une liaison avec la verticale par l'intermédiaire de ses piliers anatomiques. Si la position de ses piliers anatomiques ne le permet pas, ils sont remplacés par un pilier fonctionnel.
Positioning at the bisector of the upper end of the abdominal functional abutment.
The image below uses the heads to show the pressure application surfaces, depending on the shape of the chest. This shifts the anatomical abutments at the phrenic center, changing their relationship to the vertical. In order to function the diaphragm needs a connection to the vertical through its anatomical abutments. If the position of its anatomical abutments does not allow this, they are replaced by a functional abutment.

La mise en place d'un pilier fonctionnel abdominal est une opération complexe, mais c'est le seul moyen pour que le rachis retrouve sa liaison avec la verticale.
L'importance de l'orientation dépressionnelle centrée par les piliers anatomiques lombaires et cervicaux.
Les schémas ci dessous montrent le lien entre l'orientation dépressionnelle des piliers fonctionnels et l'accentuation de la partie supérieure de la courbure dorsale.
The placement of a functional abdominal abutment is a complex operation, but it is the only way for the spine to regain its connection with the
vertical.
The importance of the depression orientation centered by the lumbar and cervical anatomical pillars.
The diagrams below show the link between the depressed orientation of the functional pillars and the accentuation of the upper part of the dorsal curvature.

L'orientation inspiratoire en rose et expiratoire en vert déterminent la position inférieure du pilier fonctionnel expiratoire lombaire.
Avec les dessins suivants on voit par rapport aux dessins précédents que le pilier fonctionnel se positionne en avant des piliers anatomiques.

L'échappement et le pilier fonctionnel.
Les dessins suivants font apparaitre que le pilier fonctionnel post.ne peut pas se mettre en place sans un échappent pelvien du coté opposé.
The exhaust and the functional pillar.
The following drawings show that the post functional abutment cannot be inserted without a pelvic outlet on the opposite side.

Le vide pleural dans sa partie postérieure et sa liaison avec l’antéversion du bassin.
A gauche les digitations antérieures et postérieures passent par les piliers anatomiques à l’inspiration et à l’expiration.
A droite les digitations inspiratoires passent en avant des piliers anatomiques, et les digitations expiratoires passent en arrière des piliers anatomiques.
L’inspiration et l’expiration sont des mécanismes distincts.
On peut voir la zone d’occultation pressionnelle inspiratoire intestinale.
The pleural void in its posterior part and its connection with the
anteversion of the pelvis.
On the left, the anterior and posterior digitations pass through the anatomical pillars on inhalation and exhalation.
On the right the inspiratory digitations pass in front of the anatomical pillars, and the expiratory digitations pass behind the anatomical pillars.
Inhalation and exhalation are distinct mechanisms.
We can see the zone of intestinal inspiratory pressure occlusion.

Comprendre l’échappement.
Par rapport aux piliers anatomiques, pour l’insp. et l’exp. Les digitations se partagent le décrochement xiphoïdien sagittal de façon égale.
Par rapport au centre phrénique pour chaque digitation, contraction verticale et horizontale par rapport aux bissectrices.
La double orientation des intercostaux et son déploiement.
Avec l’échappement et le pilier fonctionnel l’orientation intercostale est unidirectionnelle.
Une orientation diaphragmatico-vertébrale pour les piliers anatomiques et diaphragmatico-abdominale pour le pilier fonctionnel.
Nous avons suffisamment traité les verticales des vertèbres de transition et de translation, pour que vous compreniez les rapports avec la verticale des piliers anatomiques. De même que leur remplacement par le pilier fonctionnel pour rétablir l’équilibre vertical.
Understand exhaust.
Compared to anatomical abutments, for insp. and exp. Digitations share the sagittal xiphoid detachment equally.
With respect to the phrenic centre for each digitation, vertical and horizontal contraction with respect to the bisectors.
The double orientation of the intercostals and its deployment.
With the escapement and the functional pillar the intercostal orientation is unidirectional.
A diaphragmatico-vertebral orientation for the anatomical abutments and diaphragmatico-abdominal orientation for the functional abutment.
We have covered the verticals of the transition and translational vertebrae sufficiently so that you can understand the relationship to the vertical of the anatomical abutments. As well as their
replacement with the functional abutment to restore vertical balance.

Comprendre l’échappement avec colonne sans courbure.
L’inversion des têtes traduit la correspondance avec l’expiration, donc avec les intercostaux. Dans un mouvement uniforme ils sont a orientation contraire pour se déployer ici il n’y a qu’une seule orientation.
Understanding the exhaust with column without curvature.
The inversion of the heads translates the correspondence with the exhalation, therefore with the intercostals. In a uniform movement they are in opposite orientation to deploy here there is only
one orientation.

L’orientation des angles costaux dépend de la position des bissectrices entre partie verticale et horizontale par rapports aux piliers anatomiques.
L’orientation des angles costaux dépend de la position des bissectrices entre partie verticale et horizontale par rapports aux piliers anatomiques.
De la répartition des digitations par rapport aux piliers anatomiques sur la verticale.
De la position des attaches lombaire et cervicale des piliers anatomiques et des piliers des intercostaux.
Evidemment en fonction des variations des rapports entre ces trois éléments qui sont nombreuses, vous aurez des formes différentes. Mais vous aurez toujours une relation précise entre la forme du diaphragme les angles costaux et les articulations vertébrales. Le tout étant lié à la verticale permet d’avoir une explication précise des troubles douloureux des pieds à la tête. Ce qui devrait éviter dans l’avenir bien des traitements couteux.
The orientation of the costal angles depends on the position of the bisecting lines between the vertical and
horizontal parts in relation to the anatomical abutments.
The distribution of digitations in relation to the anatomical abutments on the vertical.
The position of the lumbar and cervical attachments of the anatomical and intercostal abutments.
Obviously, depending on the variations in the relationships between these three elements, which are numerous, you will have different shapes. But you will always have a precise relationship
between the shape of the diaphragm, the intercostal angles and the vertebral joints. The whole being linked to the vertical allows to have a precise explanation of the painful disorders from the
feet to the head. This should avoid many expensive treatments in the future.

L’échappement inspiratoire diaphragmatico-intercosto-abdominal.
La poussée pressionnelle inspiratoire déplace la bissectrice en réduisant la hauteur de la partie montante antérieure du diaphragme qui accompagne la montée des côtes.
La poussée dépressionnelle expiratoire déplace la bissectrice en augmentant la hauteur de la partie montante postérieure du diaphragme.
Le déplacement de la bissectrice est un échappement car il empêche les piliers anatomiques de rester au centre. Il est bien compréhensible que les piliers anatomiques doivent rester au centre dans une fonction uniforme.
The diaphragmatic-intercosto-abdominal inspiratory exhaust.
The inspiratory pressure thrust moves the bisector by reducing the height of the anterior rising part of the diaphragm that accompanies the rise of the ribs.
The expiratory pressure thrust moves the bisector by increasing the height of the posterior rising part of the diaphragm.
The displacement of the bisector is an escape because it prevents the anatomical pillars from remaining in the center. It is understandable that the anatomical abutments must remain centered in a uniform function.

The guidelines for inspiration and experimentation should be observed here. Digitations of the diaphr. In relation to the position of the lumbar P.A. and the phrenic centre at the top. As well as the orientation of the costal angles.

Lower end of the functional pillar and orientation of the inspiratory and expiratory digitations.
Lower end of the functional pillar and orientation of the inspiratory and expiratory digitations.
P.A. interc. Cervical.
P.A. abdo.

Pilier fonctionnel et échappement insp. exp.
Orientation des digitations et des intercostaux sans croisement complémentaire.
Normalement les intercostaux sont a double orientation. Avec l'échappement ils sont a orientation unidirectionnelle.

bla

Observez la forme du thorax et la forme du diaphragme.
La forme du diaphragme vous donne la valeur des orientations pressionnelles.
La position du centre phrénique et des piliers anatomiques ou fonctionnels.
Normalement les digitations sont orientées sur le centre phrénique.
Observe the shape of the chest and the shape of the diaphragm.
The shape of the diaphragm gives you the value of the pressure orientations.
The position of the phrenic center and the anatomical or functional abutments.
Normally the digitations are oriented on the phrenic centre.

Le nombre de digitation par plan et leur orientation déterminent la forme du thorax.
L’orientation des piliers anatomiques ne permet plus leur liaison à la verticale.
The number of digitations per plane and their orientation determine the shape of the thorax.
The orientation of the anatomical abutments no longer allows them to be connected vertically.

L’image de gauche est une image à deux couleurs qui traduit la séparation des mécanismes inspiratoire et expiratoire dans le plan sagittal. Les deux hémithorax sont complémentaires à l’inspiration et à l’expiration.
Les flèches rouge concernent le mouvement des côtes il peut s’associer légèrement a l’échappement inspiratoire, mais il est surtout actif a l’expiration en se portant en avant et dedans.
L’orientation insp. et exp. est unidirectionnelle mais reste complémentaire pour les deux hémithorax.
A droite avec la scoliose non compensable les deux couleurs sont croisées. Une orientation pour l’inspiration et l’autre orientation pour l’expiration.
Dans ce cas les piliers anatomiques ne peuvent pas recevoir une tension symétrique à l’expiration.
Normalement on peut s’attendre a ce que cette tension ne soit pas symétrique. Dans ce cas à défaut d’une autre cause, les variations entre les deux piliers pourraient entrer dans le cadre des attitudes scoliotiques très fréquentes.
Jusqu'à une certaine valeur à définir, a partir de laquelle, a défaut d’une autre cause, on entrerait dans ce que j’appelle la scoliose non compensable.
The image on the left is a two-color image that reflects the separation of the inspiratory and expiratory mechanisms in the sagittal plane. The two haemithoraxes are complementary to the inspiratory and expiratory processes.
The red arrows concern the movement of the ribs it may be slightly associated with inspiratory escape, but it is mainly active at expiration by moving forward and in.
The inspiratory and expiratory orientation is unidirectional but remains complementary for both hemithoraxes.
On the right with non-compensable scoliosis the two colours are crossed. One orientation for inhalation and the other orientation for exhalation.
In this case the anatomical abutments cannot receive symmetrical tension on exhalation.
Normally this tension can be expected to be non-symmetrical. In this case, in the absence of any other cause, the variations between the two pillars could be part of the very frequent scoliotic attitudes.
Up to a certain value to be defined, from which, in the absence of another cause, one would enter into what I call non-compensable scoliosis.

Ici l’opposition entre les deux hémithorax par rapport a la verticale disparait c’est la verticale qui se déplace.
C’est sans conséquence respiratoire. Le problème interviendra avec le réglage de la position debout si le décalage dépasse une certaine valeur.
La prise en compte de cette valeur devrait permettre d’interdire la station debout sans précautions pour certains sujets.
Here the opposition between the two hemithoraxes in relation to the vertical disappears, it is the vertical that moves.
This has no respiratory consequences. The problem will occur with the adjustment of the standing position if the shift exceeds a certain value.
Taking this value into account should make it possible to prohibit standing without precautions for certain subjects.

Piliers anatomiques et piliers fonctionnels lombaires.
L’organisation musculaire abdominale est une organisation très précise.
Les moyens dont nous disposons permettent d'y avoir accès.
Anatomical abutments and lumbar functional abutments.
The abdominal muscular organization is very precise.
The means at our disposal make it possible to have access to them.

On peut voir ici la liaison des intercostaux fonctionnels et des piliers fonctionnels cervicaux et lombaires.
Ce qu’il faut comprendre c’est que les intercostaux ne sont plus croisés, ils sont a orientation unidirectionnelle donc fonctionnels.
Here we can see the connection of the functional intercostals and the cervical and lumbar functional pillars.
What must be understood is that the intercostals are no longer crossed, they are unidirectionally oriented and therefore functional.
